
At a particular drain to source voltage called the pinch-off voltage the drain current reaches the saturation level.As the drain voltage is increased the channel of conductance tends to become narrower and narrower and current at the drain terminal gets smaller.When the positive voltage is applied to the drain to source terminal of JFET and when the gate to source voltage is zero, the Drain current starts flowing and the device is said to be in ohmic region.The drain characteristics of the JFET are N-Channel JFET Characteristics Drain Characteristics of Junction Field Effect Transistor(JFET) The curves plotted in between the current value at the drain and the voltage applied in between drain and the source by considering the voltage at the gate and the source as the parameter decides the characteristics of output that are also referred to as the drain characteristics. Hence the above discussed are the operating modes involved in the field-effect transistor. These voltage values are generally specified in the data sheet. The device should not be operated under this condition. Hence the channel at the drain and the terminal source gets affected resulting in the breakdown condition. Hence the FET is considered to be fully ON at this region.Īs the value of the voltage applied between the terminals of the drain and the source is considered to be high due to this the current value at the drain tends to increase drastically. This region in FET is also referred to as Active Region. Where the voltage value at the drain and the source don’t get affected but at this region, the maximum value of the current flows from the terminals of drain towards the source. The current at the drain gets controlled by the amount of the voltage applied at the terminals of the source and gate. In this region, the behavior of the transistor turns as the conductor. But when the gate to source terminal is zero the drain current reaches the saturation level. Theoritically there should be no evident flow of the current at the pinch off condition. The resistance value at the channel present between the terminals of the source and the drain is at peak during this region. In this case, the FET acts like a resistor that is controlled by the voltage. The region at which the current value of the drain behaves linearly to the applied voltage as input at the drain and the source terminal is referred to as the Ohmic Region of field-effect transistor.
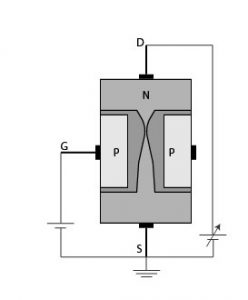
Modes of FETsĪs the voltages applied to the input terminal decides the various modes of the FET. In this case, the transistor is referred to as the resistor that is controlled by the voltage. Here current flow reaches the saturation level at the transistor.

As the value of the differences in potential increases between the terminals of drain and the source, the flow of the currents tends to be in continuous.īut the at a particular voltage at the drain and the source, the transistor reaches the condition of voltage known as the pinch-off voltage. These majority charge carriers flow is noted in a linear manner. This is the major reason due to which the flow of the majority concentration of carriers can be evident from the terminal drain to the lower potential applied terminal called source.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
